Culprit Locator (or root-cause finder) is a set of ELK-based dashboards created based on ONAP logs to identify where within a failed flow that a problem originated in the most efficient and effective way. The intention is that this would be able to help the testers, developers, and operations to get issues from identification to diagnosis/fix more quickly. This application demonstrates how the traceable logs can be used to enhance troubleshooting efforts for the testers, developers and operations. The current version is based on explicit ERROR logs to quickly locate the problem sources in terms of components or subcomponents or a series of significant log details.
We assume the index pattern "logstash-*" has been created on Kibana either by default or manual (refer to Logging User Guide Dashboard), and the following data fields are available from the latest version of onap-pipeline.conf:
In case the fields for subComponent, vLogLevel, detailmessage do not appear, check and add the following part in the onap-pipeline.conf around the end of the filter. (Not necessary to restart logstash)
ruby {
code => "
path = event.get('source').split('/')
if path[5].include? 'log'
event.set('subComponent', path[4])
else
event.set('subComponent', path[5])
end
event.set('component_subComponent', event.get('componentName') + '_' + event.get('subComponent'))
case event.get('loglevel')
when 'INFO'
event.set('vLogLevel', 1)
when 'DEBUG'
event.set('vLogLevel', 3)
when 'WARN'
event.set('vLogLevel', 5)
when 'ERROR'
event.set('vLogLevel', 10)
end
"
}
mutate { add_field => { "detailmessage" => "%{message}" } } |
The following two fields need to be manually created by the user against the index pattern "logstash-*" on Kibana scripted field page (Management → Index Patterns → scripted fields):


The code below needs to be put into the 'Script' part of the above page.
The drill-down time range is pre-set by -60 seconds to +5 seconds; the user could change the values as necessary.
if (doc['loglevel.keyword'].value == "ERROR") {
DateTimeFormatter ft = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("YYYY-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS");
Instant from_instant = Instant.ofEpochMilli(doc['Timestamp'].value - 60000);
Instant to_instant = Instant.ofEpochMilli(doc['Timestamp'].value + 5000);
ZonedDateTime from_z = from_instant.atZone(ZoneId.of("UTC"));
ZonedDateTime to_z = to_instant.atZone(ZoneId.of("UTC"));
String from_ts = from_z.format(ft);
String to_ts = to_z.format(ft);
String ReqId = doc['RequestId.keyword'].value;
String URL = "http://10.147.58.138:5601/app/kibana#/dashboard/cl_Culprit_Locator_Subcomponent_Level?_g=(refreshInterval:(display:Off,pause:!f,value:0),time:(from:'" + from_ts + "',mode:absolute,to:'" + to_ts + "'))&_a=(description:'',filters:!(),options:(darkTheme:!f),query:(query_string:(analyze_wildcard:!t,query:'RequestId:%20%22" + ReqId + "%22')),timeRestore:!f,viewMode:view)";
return URL;
} |
Take one of two approaches below to import the Kibana objects (dashboards/visualizations/searches).
Download the file Culprit Locator Kibana Objects into the user's computer (desktop/laptop).
1. On Kibana browser import the file: Management→Saved Objects → Import.
2. Refresh the Kibana browser and check if the objects are properly loaded.
Download and uncompress the tar file culprit_locator.tar into any directory of the ELK server, where elasticsearch is accessible; not necessary to move it into containers.
1. The default host and port is set to "localhost" and "30254". If different, open the shell script "cl_insert_kibana_objects.sh" and provide correct HOST and PORT values.
2. Run the script on the command line.
3. Refresh the Kibana browser and check if the objects are properly loaded.
How To Use
This explains the basic features of current version of Culprit Locator. The users are encouraged to take advantage of the full flexibility of Kibana features to modify and enhance the dashboards to their puporses and preferences.
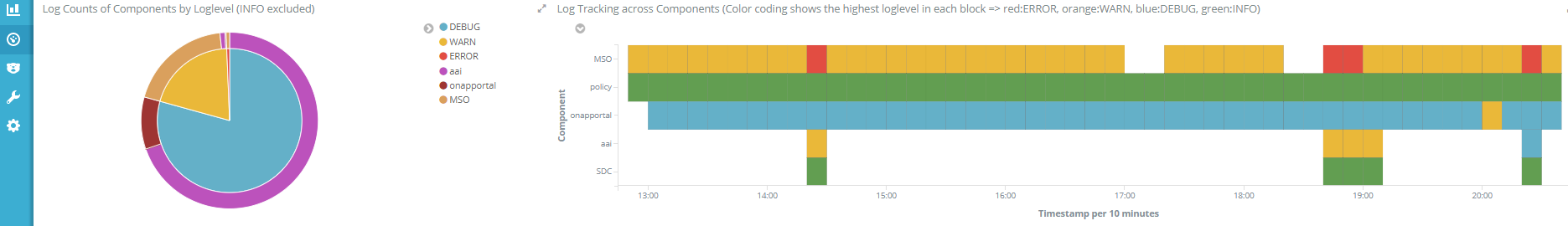
1. Open Dashboard "Culprit Locator (Component Level)" and adjust the time picker for the parts you're interested in or choose one like "Last 7 days". The dashboard features:

To investigate the logs associated with a specifc RequestId, put the RequestId in the search box like below and adjust the time period to locate the logs you want to see. (Note) RequestId should be quoted for the correct search query.

2. Drill-down (or more focused) view dashboard automatically opens on a separate tab with time perid set ranging from -60 seconds prior to the error time to +5 seconds after the error occurred. The user can continue to zoom in or click the boxes. The dashboard features:
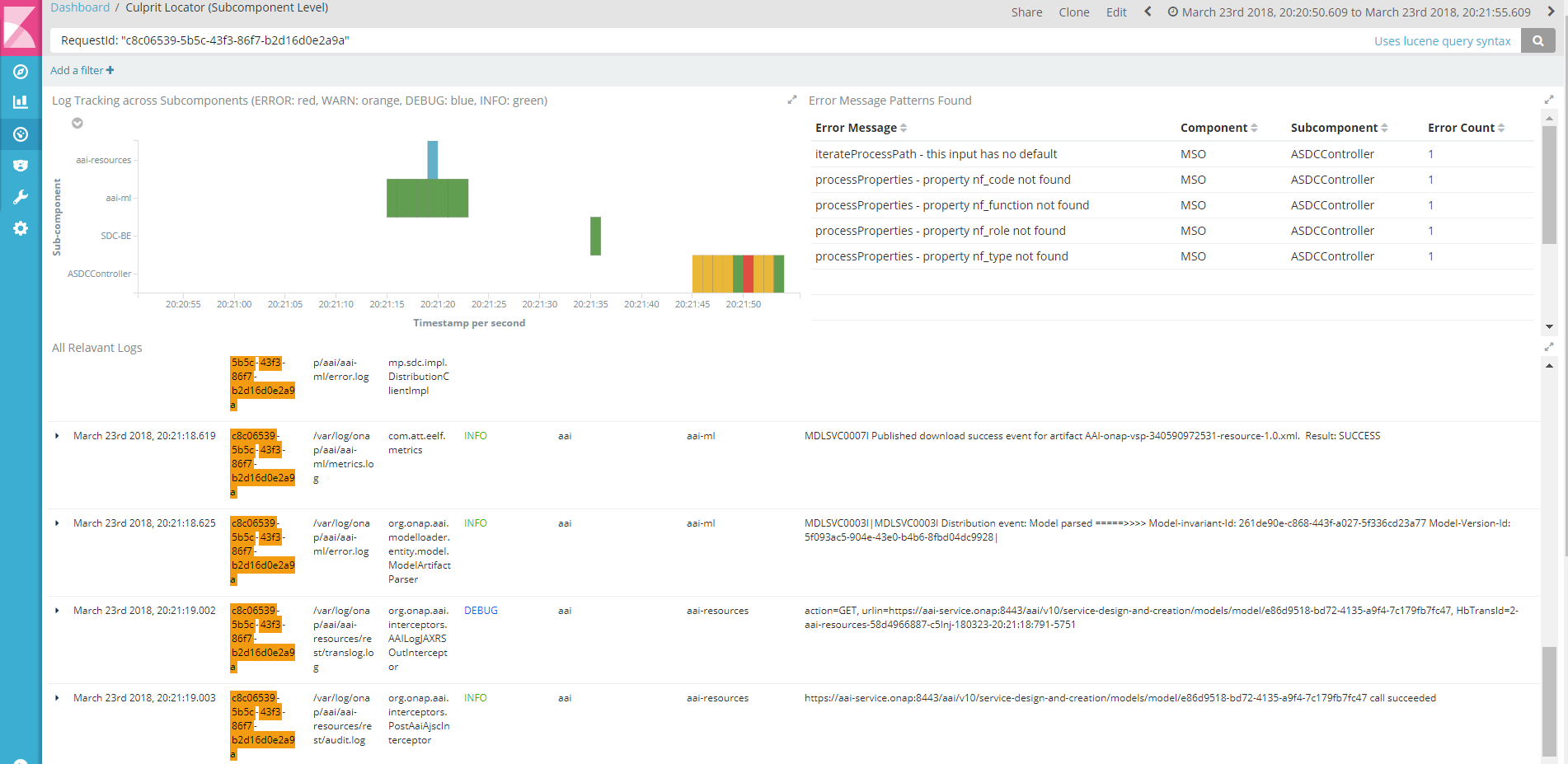
Below is a sample zoomed-in view of the red box in the previous view:

The next-step of Culprit Locator is to automate the identification of root causes with more intelligent features.