The following diagram illustrates the overall Modeling process:
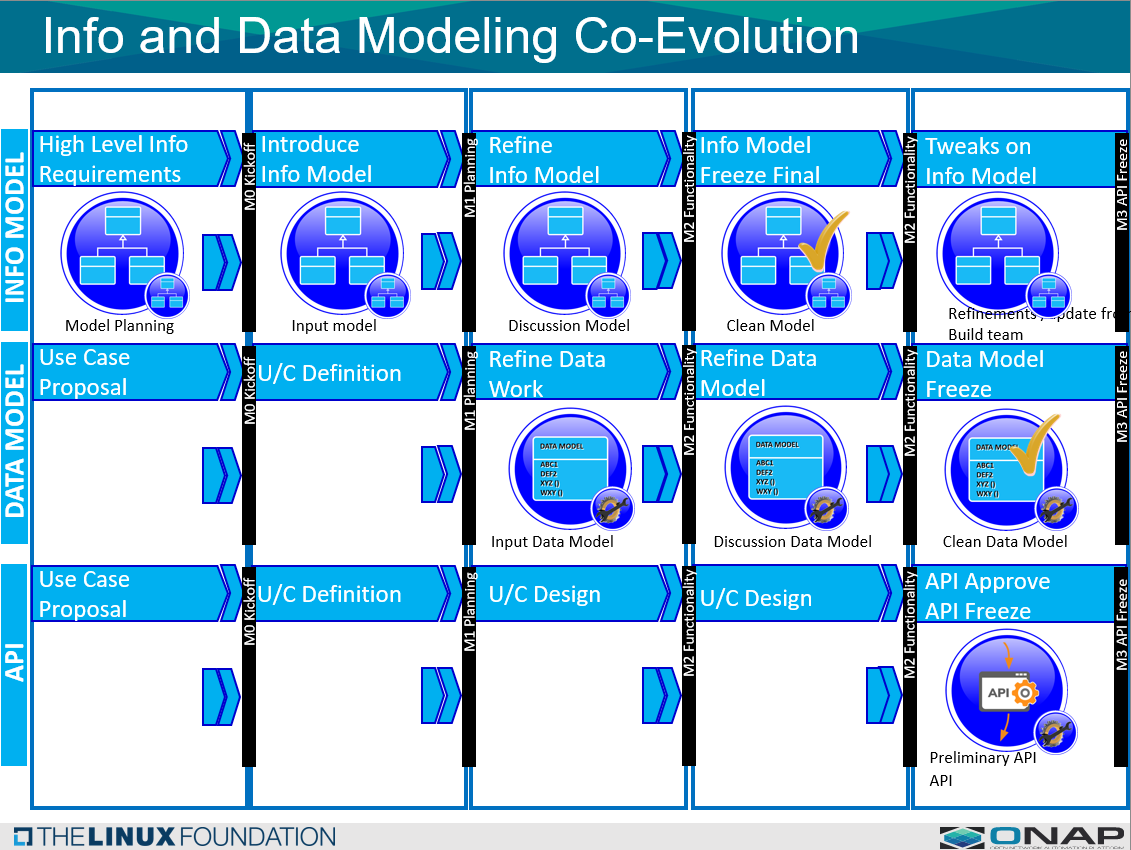
The following diagram shows the Information and Data Model co-evolution and interaction flow:
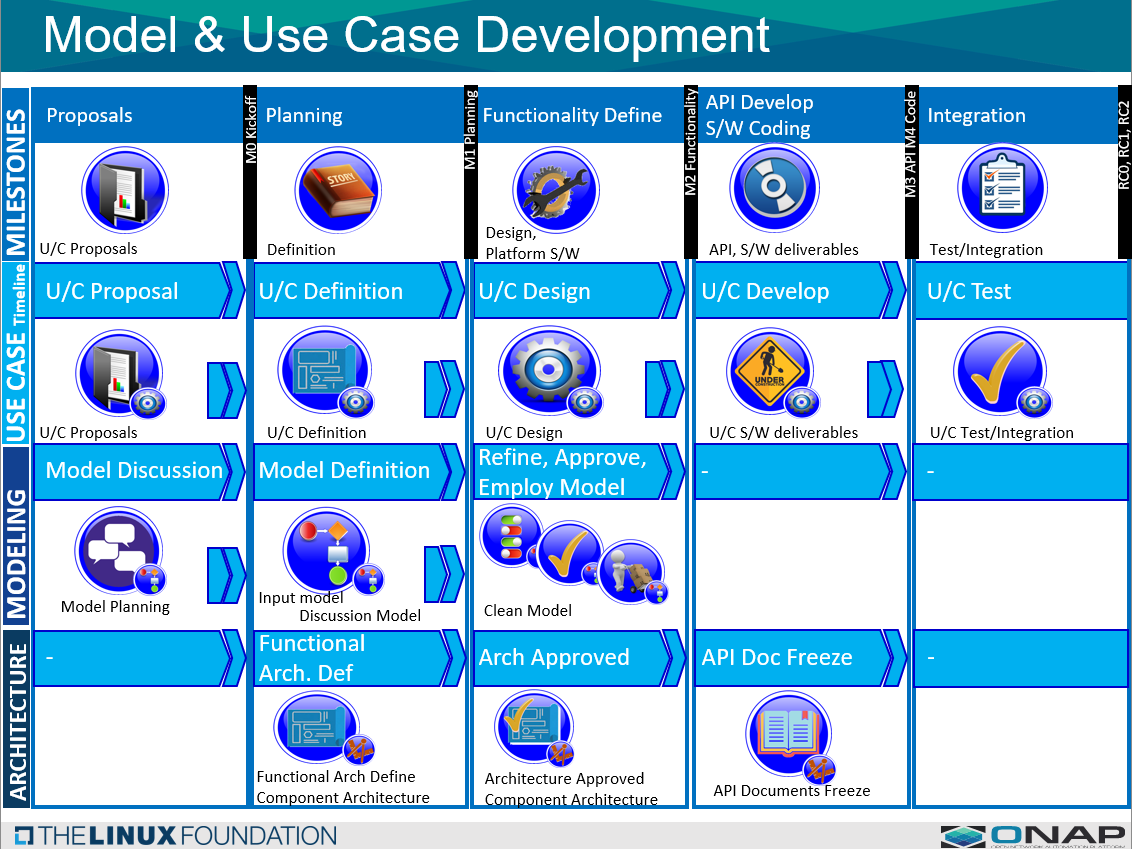
The following diagram shows the modeling process in more detail:
Proposed ONAP Process Improvements
No Modeling Presence
Add Modeling Swim Lane
Add Modeling Artifacts for appropriate milestones to Modeling Swim Lane
MO
- Modeling team does MODEL PLANNING. The planning develops into “High Level Info-model Requirements”. These High level info-model requirements fall into 3 categories:
- #1: NEW USE CASES - items from the expected Use Cases in the release (Scope of modeling, continuing, introducing, standards updates).
- #2: REFINING EXISTING MODEL - There are also Existing high level info-model requirements and the current release is focused on continuing or refining the model. Existing in a component that hasn't made it to the information model. Previously at design build-level that needs to be added into information model. For example, a need might have arisen in development but wasn't formalized. Long-lead, multi-release items might fall into this category. coded previously but no Use Case.
- #3: FORWARD LOOKING WORK (FLW) - Forward thinking requirement. For example, suppose there were a very large use case/requirement or project that is expected to come down the pipe, but if no advanced modeling work were done on it, it wouldn't make the current release. Thus, a model might be proposed in advance of the actual use case/requirement.
- Use Case Team (evaluating U/C proposals) presents their modeling needs. Each of the Use Case teams needs to come to the modeling S/C meetings to present their expected modeling needs and open a dialogue about potential model impacts so that they can be developed.
- Architecture understanding reference model. Modeling S/C members should be aware of any updates to the current release's reference model so that potential can be known.
- PTL - High level release scope from PTLs (understand from ONAP components what updates)
- PTL - Joint PTL sync meeting
- Modeling team does MODEL PLANNING. The planning develops into “High Level Info-model Requirements”. These High level info-model requirements fall into 3 categories:
M1
- Modeling team The info-model plan is established. The model planning follows a template that is worked. For example in R6 (Frankfurt) it was here: ONAP R6 Modeling High Level Requirements.
- #1: MODELING REQUIREMENTS - A description of the modeling requirements are given in more detail.
- #2: Use Cases Relevance - The relevance use cases are identified and Use Case teams can give more detailed explanation for use case requirements and how they tie to the high-level requirements. This allows for experts in Info-model team to identify what fields of existing info model could be enhanced and become aware of where the impacts are.
- #3: Impacted Projects - The impacted projects (e.g. SO, VID, SDC etc) are identified and how they tie to the high level modeling requirements
- #4: Overlapping proposals - Overlapping proposals from different use cases or forward looking work (FLW) are identified.
- #5: Model Reuse - During this time, overlap from different proposals that are evaluated can also lead to identifying where model reuse can occur.
- #6: Owner - The owner(s) for the item are identified
- #7 Priority - A priority is identified for the info model requirements. A suggested High/Medium/Low is sufficient at this stage.
- #8 Lower priority - Lower priority requirements are generally considered as "nice to haves".
- #8 Documentation after implemented - When the model plan is established, modeling requirements documentation after implemented can be worked on.
- #9 FORWARD LOOKING WORK (FLW) - FLW is another class of requirements which are intended to recognize future needs.
This is separate from the ASAMI stereotype view "Experimental" because you can get consensus from the modeling team and the PTL.
- Use Case Txeveloped.
- Architecture uxn be known.
- PTL - Hixl
Project Planning / Functional Architecture Defined / Architecture Approved
Add “Infomodel Plan Established”
Note: Infomodel Updates Begin / Data Model Refinements Begin (M1.5)
- Note: Development Commitments for Infomodel Requirements?
- Modeling team The info-model plan is established. The model planning follows a template that is worked. For example in R6 (Frankfurt) it was here: ONAP R6 Modeling High Level Requirements.
M2
Functionality Freeze
Add “Infomodel Freeze” (Approval)
Add “Data Model Freeze” (Approval)
Note: Feed to Data Dictionary??
M3
API Freeze
Add “Infomodel Final”
Add “Component Data Model Final” (Approval – Design Level Compliance)
M4
Code Freeze
Kickoff Information Model Requirements for Next Release
RCx
Runtime Compliance
Observations
Establishes and Evolves a Common Model
Project (Component) Team Involvement in Modeling Solution
Governance of Common Model and Corresponding Component Models
- Update possible in M3 and M4 (bug fixes) per exception process
Artifacts
Information Model Artifact Contains
Classes
Relationships with Multiplicity
Important Attributes with Multiplicity
Definitions
Data Types
Feed to Data Dictionary
Tooling - Papyrus with GitHub
Component Data Model Artifacts (Implementation Specific)
Component Data Model
Contains objects, attributes, & relationships (more detail than information model)
Mapping to Information Model
Feed to Data Dictionary?
API Artifacts
API Model
Mapping to Information Model
New Roles – Model Governance
Information Model
Internal Committers
Internal Approvers
Impacted Project (Component) Approvers
Impacted API Approvers
Architecture Group Approvers
Component Data Models
Internal Committers
Modeling Team Approvers
Architecture Approvers
Impacted API Approvers
API Definitions
Modeling Team Approvers
Impacted Project (Component) Approvers
Architecture Approvers
Benefits
Establishment and Evolution of a Common Model (Model Consistency)
Continue Move Toward a Model Driven Design
Improve Data Quality
Modeling S/C, Use Case Team and Architecture team touch points, interactions and cooperation:
SUPPORTING DOCUMENTS
| DOC | FILE |
|---|---|
| Way of Working (Modeling S/C, Use Case Teams, Architecture) |