Table of Contents
1. Scope
DESCRIPTION: RunTime DB is a data lake repository for configuration and operational parameters. Run Time DB is a common service component that ONAP components can access write and read information to.
WHEN EXECUTED: This information flow is used during Run Time, when configuration or operational 5G RAN physical/logical topology information (SDN-R) Core & RAN elements. 5G Configuration, provisioning of a 5G Network. SDN-R should contain the 5G Network Topology. CM Audit. CM Mediation. CM run-time storage / data persistency (MariaDB)WHEN EXECUTED: During Run Time, when data is written to the Runtime DB.
- Flow 1 - VES Configuration information coming from PNF via e.g. CM Notify
- Flow 2 - New xNF is added or deleted from ONAP; A&AI notification xNF update
- Flow 3 - Controller writing & updating operational information
- Flow 4 - Data is read from RunTime DB
PURPOSE: RunTime DB serves as a data lake as a common service and data layer for ONAP components and micro-services.
INFORMATION PASSED: Configuration information (from CM Notify) or operational information (derived during ONAP operations).
ACTORS:
- RunTime DB
- Operations Specialist (ONAP user)
- Controller, A&AI, VES collector/DMaaP
For more information and exploration details you can visit the RunTime DB Use Case Wiki at: 5G CONFIGURATION (RunTime DB)
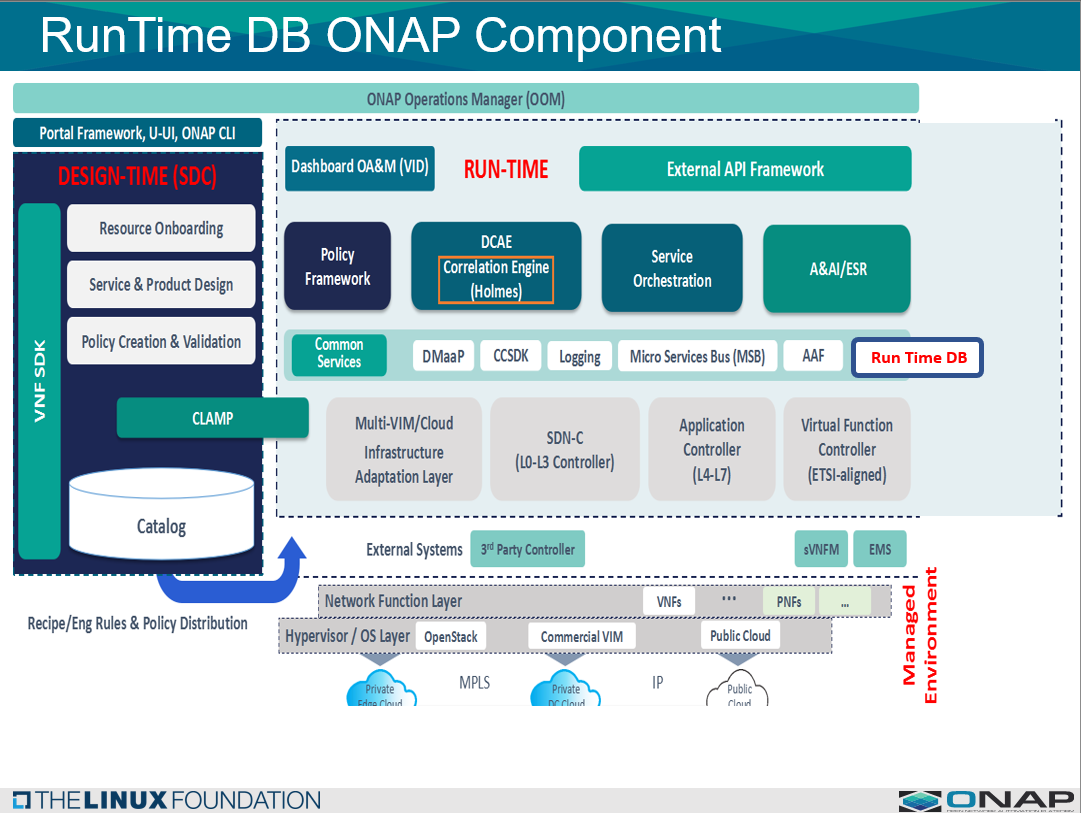
OVERVIEW RUNTIME DB
See theThe: ARC RunTime DB Component Description - R6 Frankfurt
A wiki describes a more detailed figure and description of the component.
PURPOSE OF RUNTIME DB:
REPOSITORY - The types of data that is stored in the Run-Time data storage repository for:
(1) CONFIGURATION PARAMETERS used by xNFs in run time. For example 5G Network run-time instance configuration information. and
(2) OPERATIONAL PARAMETERS used by ONAP and xNFs. Exo-inventory information is information that doesn't belong in A&AI.
- DATA LAKE - It is designed to be a common services data layer which can serve as a data lake.
- SYNCING - The RunTime DB enables the ability to sync data between ONAP & the xNFs. (The source of truth can be define).
- CM FUNCTIONS - Enables OSS configuration, optimization, and LCM operations. (FUTURE)
- CM FUNCTIONS - Enables future CM & Data management functions such as xNF Crash restoration, data restoration, data history management and auditing. (FUTURE)
- CENTRAL/DISTRIBUTED - Because it is a common service, it is part of an ONAP installation, so it could be deployed with either an Edge ONAP installation or a centralized ONAP installation. (FUTURE)
- SCOPE - The Run Time DB could also serve as the data storage to store for example ONAP Policy Rules, CLAMP Control Loop, Operational Views (FUTURE) and also accommodate other resources.
ACCESS TO RUNTIME DB (READ/WRITE):
- READ ONLY - Run-Time parameters can be READ by any ONAP platform component and any ONAP plug-in. Examples of ONAP platform components are A&AI, SDC, SDNC etc.
READ/WRITE - Parameters can be READ/WRITE from Controllers, DCAE (future), VES Collector/DMaaP, A&AI, Policy/CLAMP (future) and other components with permission settings.
- DEFAULT - SO (future), DCAE, A&AI, Controllers (CDS, APPC, SDNC) will have default read/write access to RunTime DB
- DEFINABLE - Other components will have default read-only access to RunTime DB but can be given Read/Write access on a per record basis.
SYNCING (INVENTORYNEW xNF ADDED or DELETED (A&AI):
ELEMENT SYNC - Software keeps the A&AI elements with the elements in the RunTime DB in Sync.
- A&AI - A&AI is still the master of valid entities in the network and provides a dynamic view of the assets (xNFs) available to ONAP
- RUN TIME DB - The RunTime DB is a master of the associate (exo-inventory) data associated with the entities.
- DYNAMIC VIEW - When a xNF appears or is removed from the system, RunTime DB records will be added/removed based on A&AI entries.
...
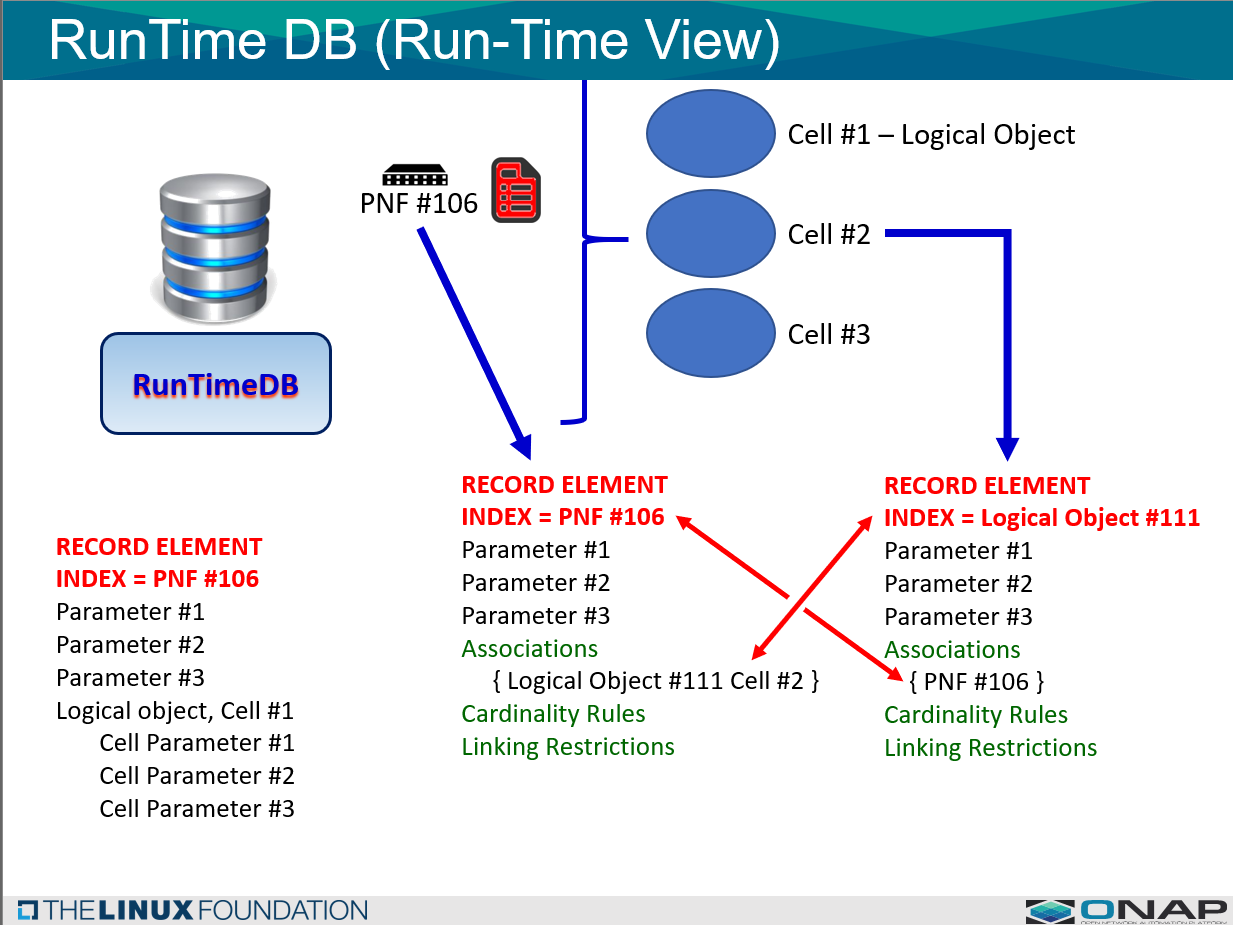
- INDEXING - Data Records will be indexed by xNF (VNF, PNF, ANF).
- RETRIEVAL - How are data records retrieved efficiently. This relates how the records are indexed.
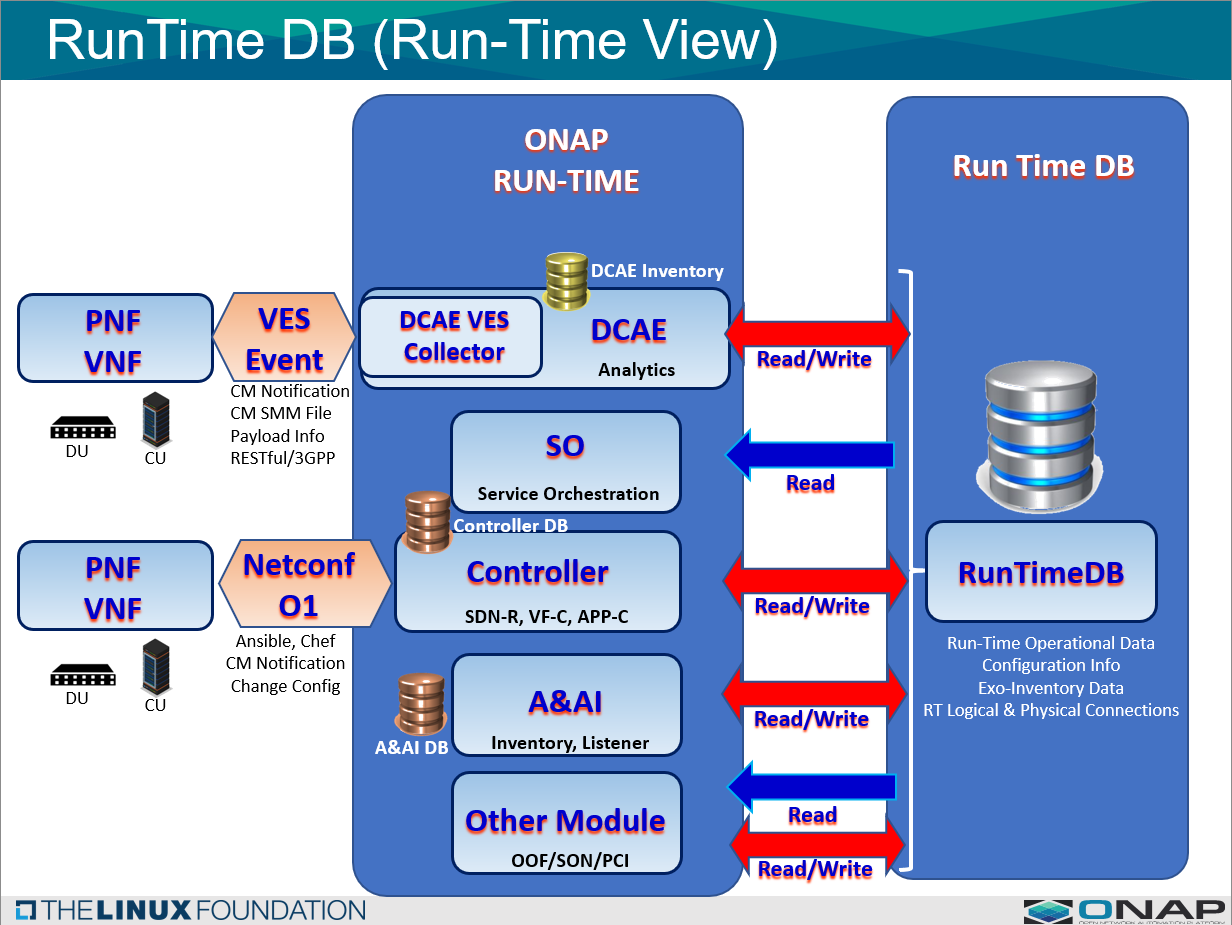
The above diagram shows the usage of RunTime DB
It shows the four basic flows captured in the diagram.
- Writing information from a VES CM Notify
- A&AI xNF addition/deletion
- Operational information written
- Information being read from the RunTimeDB
OVERVIEW RUNTIME DB INFORMATION FLOW
...
Information Flows to Run Time DB or from RunTime DB
1 INFORMATION FLOW DATA WRITTEN TO RUNTIME DB:
Information Flows to Runtime DB
New Information is written to RunTime DB from a Component or a Micro-service
The following three basic flows are described:
- FLOW 1: VES Event Updates - Information flow
- FLOW 2: A&AI xNF (create/delete) updates - Information flow
- FLOW 3: mS / Controller / Component Updates for operational inforation - Information flow
2 INFORMATION FLOW DATA READ FROM RUNTIME DB:
Information Flow from RunTime DB
...
Taking information from RunTime DB and using it to send to xNF components
- FLOW 4: Data is read from RunTime DB
2. Pre-Conditions
ONAP is ready & running:
- ONBOARDED ARTIFACTS - (future) If dynamic setup is used, definition artifacts are onboarded and used to setup the RunTime DB structures
- ONAP SOFTWARE - There is an ONAP installation. Software images loaded in OpenStack installation, where instantiation will happen (since no S/W image repository). Need to be available in Target Cloud Instances.
RunTime DB RunTimeDB is setup (Design Time):
- RUN TIME DB SETUP - RunTime DB has been setup properly and is ready to be used.
- DESIGN TIME ACTIVITIES - Design time activities have happened.
2.1 RUNTIME DB DATA STRUCTURE
2.1.1 DATA STRUCTURE (ONBOARDING & DESIGN TIME)
A data structure which is common for all different vendor xNFs will be used for the RunTime DB.
...
Any micro-service or ONAP platform component can define information in the data structure.
Before RunTime, the RunTime DB is setup with the appropriate data structures that it needs to work with.
A Yang Model definition file is used to STATICALLY define the records that RunTimeDB will manage.
2.1.2 RUNTIME DB DATA LAYER
...
The RunTime DB is a Data layer common service data lake.
There has been quite a bit of discussion related to how to architect the RunTime DB component.
In R6 is was determined, that it should be a common service as a data layer to other ONAP components.
3. Information Flow
These four flows show the usage of RunTime DB
- FLOW 1: VES Event Updates - Information flow
- FLOW 2: A&AI xNF (create/delete) updates - Information flow
- FLOW 3: mS / Controller / Component Updates for operational inforation - Information flow
- FLOW 4: Data is read from RunTime DB
3.1 FLOW 1: VES Information Flow - Writing to RunTime DB
The following UML diagram shows the Information Flow for RunTimeDB
...
RunTime DB gets the Event and updates the information
3.1 FLOW 2: xNF Addition/Delete A&AI Update Flow - Updates to RunTime DB
The following UML diagram shows the xNF Update flow from updates in A&AI for RunTimeDB
...
ADDITION - If AAI determines that a new xNF is added to the network, then RunTime DB needs to setup a new record for that xNF with the default data structure and configuration. Default Configuration is setup.
3.1
...
FLOW 3: mS/Controller Operational Info Update Flow - Writing to RunTime DB
The following UML diagram shows Where another ONAP component or Micro-Service updates the RunTimeDB
...